NEW DELHI: Retail inflation plummeted to a 75-month low in May as food prices eased sharply. It is expected to moderate further in June, which may prompt the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to hit a pause in its rate-cutting cycle after undertaking a “jumbo” cut earlier this month to support growth in the face of easing price pressures.Data released by the National Statistics Office (NSO) on Thursday showed retail inflation, as measured by the consumer price index (CPI), slumped to 2.8% in May, below the 3.2% in April. It is the lowest year-on-year inflation after February 2019 and is the fourth consecutive month when it has stayed below the RBI’s 4% target.
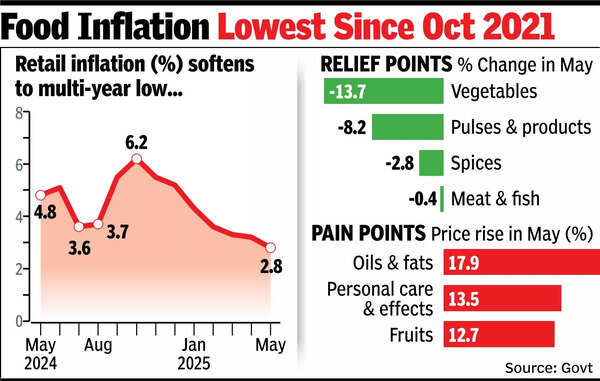
Food inflation eased to nearly 1% in May, with a sharp decline of 79 basis points during the month compared to April. Food inflation in May is the lowest since October 2021. Rural inflation was at 2.6% in May, while urban inflation was at 3.1%. The data showed vegetable prices fell 13.7% in May, while pulses and products declined 8.2% during the month, and spices fell 2.8% in May.“While till Q3 FY26, we expect CPI inflation to remain less than 4%, it may only increase in the last quarter of the current fiscal. We expect average CPI inflation for FY26 would be around 3.3%-3.5% (RBI: 3.7%) as against FY25 average of 4.6%,” said Soumya Kanti Ghosh, group chief economic adviser at SBI.“Given this benign inflation expectations on the back of a 50 basis points rate cut recently in June policy, the current focus of RBI is to support the momentum in capital formation for more durable growth. We expect a pause in rate action here onwards till the Dec 2025 policy, though a lot will depend upon incoming data,” said Ghosh in a note.

































